Phishing Attack Examples and How to Prevent them
Phishing is arguably the most successful cyber-attack method on the planet. Cybercriminals love to phish people because phishing works. Phishing is a type of social engineering that manipulates employees and individuals into performing actions that benefit a cybercriminal. There have been many research studies into the success rate of phishing; the statistics vary, but they all agree that it is the most utilized method to begin a cyber-attack against an organization. The latest research from Symantec shows that 96% of data breaches start with a phishing email; 1 in 4,200 emails during 2020 was phishing email. Further research from Verizon's 2021 Data Breach Investigation Report shows an upwards trend in phishing-related cyberattacks.
Phishing is successful and damaging, the results of which can be ransomware, a Business Email Compromise (BEC) scam, data breach, identity theft, and so on. Therefore, it is vital to understand the different types of phishing and the types of cyber-attacks associated. Both organizations and managed service providers (MSPs) can use this know-how to understand better how to prevent phishing attacks.
Did You Know?
SpamTitan's spam catch rate
a ransomware attack occurs
the average cost to manage spam per person without an email filter
of all email is spam
Phishing Attack Examples
Email Phishing
This is the most common form of phishing and one that most of us have come across. This type of phishing uses a spray gun approach to phishing. Cybercriminals indiscriminately send out phishing emails to any email address at their disposal. Scammers can quickly obtain thousands of email addresses by harvesting or from email addresses stolen in data breach incidents. Phishing emails contain links to a malicious website or an infected attachment.
What Happens in Email Phishing Campaigns?
Phishing emails are regular occurrences in both private and corporate email inboxes. These phishing emails often impersonate known commercial brands such as PayPal, Apple, and Facebook. These emails will use an individual's trust in that brand to manipulate their behavior. Phishing emails use tactics such as fear of hacking, urgency, or fear of missing out (FOMO) to encourage an email recipient to click on a malicious link or download an infected attachment.
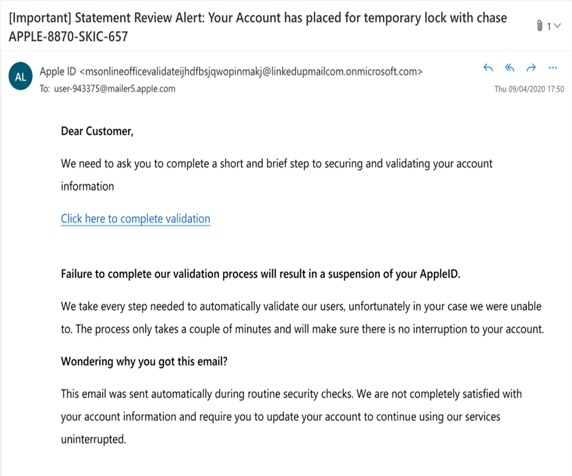
Example of an AppleID phishing email
Email phishing can lead to malware infection via an infected attachment in the email. If the recipient clicks on the attachment, the malware will look for vulnerabilities in software on the user's device and exploit these flaws to install the malicious software. Emails must be scanned and threats detected.
Email phishing can lead to stolen login credentials via an associated spoof website, a user taken to this site if they click on a link in the email or an attachment.
Phishing emails are increasingly challenging to detect as they are designed to evade end user detection. For example, infected attachments such as Word and Excel documents are now less common, and instead, fake image files (.jpeg and .png) are increasingly used to bring malware into people's inboxes.
Spear-phishing
Spear-phishing is a targeted form of email phishing. An Avanti report found some worrying results when investigating changes in phishing volumes. The researchers found that 85% of respondents spoke of "increasing sophistication" in phishing campaigns. Email phishing works, but spear-phishing takes phishing to new levels of success. Phishers take advantage of a lack of IT skills in an organization to exploit a stressed and tired workforce. Suppose a scammer can get the castle's keys (login credentials to corporate networks/apps); they can make a lot of money and cause damage. Spear-phishing targets those in an organization who have access to sensitive corporate resources, such as system administrators, C-level executives, and those working in accounts payable. Phishing emails work in the same way as email phishing, using psychological tactics to manipulate the behavior of their target.
What Happens in a Spear-Phishing Campaign?
A scammer will typically carry out reconnaissance research into a company. This will help them locate a likely target, such as a system administrator, who will have the privilege level to giving the scammer access to sensitive resources. For example, the scammer will compose a realistic-looking email that may spoof a corporate app like a Microsoft Office 365 request to download a vital company document. Suppose the target employee clicks on the malicious link and enters their login credentials or other revealing data into an associated spoof website. In that case, the scammer will use this to carry out the next stage in the attack, e.g., infect the network with ransomware.
Whaling
When spear-phishing scammers go after C-level executives, the phishing attack is known as 'whaling,' aka, catching the big one, a 'whale'. In whaling attacks, scammers will carry out deep reconnaissance of a company, building up the profile of a C-Level executive, such as a CEO or CFO. The resultant spear-phishing email will use extreme tactics and behavioral motivators, such as fear, to manipulate the executive's behavior. For example, the phishing email may contain a threat that the company will be sued to encourage the executive to click on a link or open an infected attachment.
What Happens in a Whaling Attack?
Business Email Compromise (BEC) often has an element of whaling involved. Large and small firms are both at risk of whaling, as this NPR interview with a small business owner discussed: "Mark," an owner of a real-estate firm, told the show how he became a victim of a targeted account takeover attack. Whaling attacks typically try to trick an executive into transferring money or by encouraging a C-level executive to pass approval for the transfer of funds to an accounts payable employee.
Clone phishing
Clone phishing is a clever variation of Spear phishing that uses even more sophisticated social engineering tactics. Clone phishing is so-called because the primary technique used by fraudsters is to clone a legitimate email and use that to trick victims. The cloned phishing emails used in this phishing variation are usually based on mass-distributed business emails; for example, an invitation to an online webinar or an urgent request to verify your account with a 'well-known' brand. To generate a cloned email, the hacker first intercepts the target business email; emails are intercepted using several techniques, including unencrypted email channels, which can lead to Man in the Middle attacks (MitM). Once the hacker has a copy of the email, they create a cloned copy with the exact wording, branding, and content as the legitimate email. However, the hackers will insert a malicious link or an infected attachment during email cloning. Once completed, the cloned email is then sent out to the target company employees and contacts.
A recent Google Docs phishing scam that affected over 1 million Gmail users – PhishTitan had 100% success rate in defending our users against this threat.
What Happens in a Clone Phishing Attack?
In the run-up to a Clone phishing attack, the attackers will have conducted intelligence on the target company. During the construction of the cloned email, the attackers will add malicious elements, such as an infected attachment or a link to a spoof website. The hackers will ensure that the spoof website matches the target brand. If a Clone email recipient clicks the malicious link in the cloned email, they will end up on the spoof website, which is engineered to steal login credentials and other data. If login credentials are stolen, they will be used to gain unauthorized access to corporate devices and the network. Once the hackers have access to the corporate apps and network, they will use that access to further attacks on the organization. These attacks include infecting the network with ransomware, stealing data, and committing fraud such as Business Email Compromise (BEC) and other financially motivated cyber-crimes. Even if the login credentials stolen are not privileged credentials, hackers will use techniques such as lateral movement to escalate login privileges. Recent research shows that phishing is becoming the most common method to deliver ransomware, with Q3 2022 showing a surge in the use of phishing for ransomware infections.
Vishing
Vishing is a form of phishing that uses a mobile phone to extract information from an individual or direct them to carry out a behavior that results in stolen data. Often vishing is used in combination with other phishing types, such as spear-phishing. Whaling, for example, may involve an initial phone call from a scammer to extract information that then leads to a whaling email. Vishing covers a spectrum of sophistication, from spray gun-type vishing messages that target the public to focused spear-vishing. The latter may work as part of a scam that steals large sums of money from a business. An excellent example of this was a 2018 scam that involved a phone call that used a fake voice to trick a CEO into transferring $240,000 to a fraudster.
What Happens in a Vishing Attack?
A recent FBI notice explains how scams may use multiple steps during a cyber-attack, some of these steps focusing on privileged users. These attacks often involve reconnaissance using vishing that then utilizes spoof web pages that are used to steal second-factor authentication codes, thereby bypassing traditional forms of protection.
The APWG recorded the worst-ever period for phishing in the first quarter of 2023, with 1,624,144 phishing attacks.
Smishing
Smishing is a form of phishing that uses mobile messaging channels, such as SMS text and WhatsApp, etc., to send out a phishing message. Like its email counterpart, the smishing message uses psychological tricks to manipulate targets.
What Happens in a Smishing Attack?
Like all social engineering attacks, smishing uses tricks to manipulate users into doing as the scammer wants. The fraudster uses tricks such as instilling fear into the recipient of a phishing message: financial smishing is a form of smishing where the message will look like it is from a well-known bank. The message will be composed to scare the recipient into thinking their bank account is compromised. The smishing message typically contains a URL that will take the person to a fake bank website where their actual bank login credentials will be stolen, and their bank account hacked.
Barrel phishing
Barrel phishing or "Double-Barrel" phishing is successful because it uses emails to build trusted relationships with the victim. Barrel phishing uses a double-whammy email system of 'bait and sting': the first or 'bait' email is sent to the target to help make the victim feel that a legitimate person is emailing. This bait email is then followed by the second part of the Barrel phishing attack, i.e., the 'sting' or malicious email. Trust is the core element of a Barrel phishing attack; the attacker uses the bait email to build a trusted relationship with the email recipient. This trust is then exploited in the follow-up email containing malicious elements. Barrel phishing attacks are designed to steal login credentials and other data that is used in other cyber-attacks, including Business Email Compromise (BEC) and ransomware infections.
What Happens in a Barrel Phishing Attack?
Barrel phishing attacks work by building a trusted relationship to ensure a successful attack. Any targeted phishing attack will require the cybercriminal to conduct intelligence-gathering exercises to find out as much as possible about the target. Once the attacker has the information needed, they will create a believable first email that is non-malicious. This first email typically reflects a brand or company known to the victim to help build rapport. The first Barrel email is designed to engage the recipient and make them feel comfortable and trust the sender. Soon after delivering this first non-malicious email, the second Barrel email will be sent to the same recipient. This second email does contain malicious content. Because the first email was a relationship-building exercise, the recipient is more likely to engage with any links or attachments in this second email. They will be sent to a spoof website designed to steal login credentials or other sensitive data if they click a link. Alternatively, the second Barrel email may contain an attachment; if the victim opens this attachment, it may end in ransomware or other malware infection. Barrel phishing is a first part of a chain of attack that can end in financial scams, such as Business Email Compromise or ransomware attacks; the Ponemon Institute found that 54% of security incidents were caused by credential theft.
Ponemon Institute found that 54% of security incidents were caused by credential theft.
Fake websites
Many phishing campaigns are dependent on fake websites to carry out an attack, so it is essential to note the part that spoof websites play in email phishing attacks. Fake or spoof websites are typically sophisticated and realistic, using similar domain names to the brand they spoof. In addition, the sites usually use digital certificates to make the website look 'secure' - the certificates setting the site URL as beginning with an HTTPS (S for secure).
What Happens if a User Navigates to a Spoof Website?
The spoof website is often a companion to a phishing campaign. A malicious link in a phishing, spear-phishing, or smishing message, will take a recipient to the companion spoof website. The fake webpage usually reflects the brand that the phishing message spoofs, for example, a Microsoft Office 365 login page. Once the target has navigated to the spoof website, they are requested to enter their login credentials (or other personal details). Once submitted, the data is sent to the hacker behind the scam, who then uses them to log in to the actual site.
Verizon’s 2023 DBIR found that 36% of all data breaches involved phishing.
Ways to Stop Phishing in all its Forms
Protection against phishing requires a layered approach to anti-phishing protection; by using multiple layers of protection, an organization is more likely to stop the threat before it becomes an incident:
Educate your employees
This is a fundamental step in phishing prevention. Security awareness training, augmented with simulated phishing exercises, will make employees aware of the various phishing attack methods.
Use an Email Filter
Prevent phishing emails from landing in an employee's inbox using a multi-layered spam filter. The filter must be configurable to allow legitimate emails to keep phishing emails out.
Deploy Content Filtering
Any navigation to a fake website, such as via a mobile device, can be prevented by deploying a content filter. For example, an HTTPS content filter checks a website to ensure it is not a phishing site before allowing a user to enter the site; any sites identified as phishing are blocked.
Choose a Phishing Prevention Platform that is Easily Deployed and Maintained
Effective phishing prevention needs to be scalable across multiple types of devices. The email and content filters must be able to be easily configured and updated from a central console. A cloud-based system provides central management and is suited to deployment and management from a managed service provider (MSP)

Susan Morrow
- DATA PROTECTION
- EMAIL PHISING
- EMAIL SECURITY
Talk to our Team today

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is an Email Phishing Filter?
Cyber-criminals use phishing email messages to steal corporate network credentials or install malware on a user’s local machine. An email phishing filter blocks malicious messages from reaching the intended recipient and protects an organization from data breaches and insider threats. For every email blocked by an email phishing filter, an organization reduces its cyber risks.
What are Good Anti-Phishing Solutions?
Anti-phishing solutions must block malicious email messages from reaching their intended recipient. Organizations can implement failsafe options such as antivirus in case of a false negative, but a good anti-phishing solution uses artificial intelligence to block sophisticated zero-day attacks. PhishTitan is a proven well-rated anti-spam solution used by enterprises and managed service providers.
What Does a Phishing Filter Do?
Instead of allowing users to receive spam and malicious email messages, a phishing filter blocks phishing, malware, or email messages with malicious attachments from reaching the intended recipient. Artificial intelligence (AI) is used to detect malicious messages, including zero-day threats. Malicious messages are sent to a quarantine section where administrators can review them.
Which Products Help Protect Users Who are Prone to Clicking on Phishing Scams?
There are two ways to prevent users from clicking on phishing emails. The first is to prevent malicious emails from arriving in the inbox in the first place. The second is to provide point-of-click protection for users who accidentally click on malicious emails that get through. Adequately protecting your organization against phishing threats requires a multi-layered defense.
Does Filtering Phishing Emails Work?
Yes! The vast majority of phishing emails come with tell-tale signs of malicious intent. Technologies like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC allow email providers to automatically filter out harmful emails that human users may not recognize.
What Happens when Phishing Filters Incorrectly Block an Incoming Email?
False positives happen when security technologies incorrectly flag legitimate data as malicious. This risk comes with all security solutions – not just phishing filters. However, high-quality security products produce fewer false positives than lower-quality competitors.
What Separates the Best Anti-Phishing Solutions from the Rest?
High-quality anti-phishing solutions must protect email users by preventing malicious emails from entering their inboxes, and providing point-of-click protection against malicious URLs and attachments embedded in emails. These two features are essential for adequate email security.
Doesn’t Microsoft 365 Already Have the Best Anti-Phishing Solutions Built in?
Microsoft is responsible for many impressive security technologies, but phishing protection is not one of them. Microsoft 365 doesn’t consistently keep phishing emails out of users’ inboxes and doesn’t offer reliable point-of-click protection to prevent malware infection. As a result, Microsoft 365 users need more protection.
Can Anti-Phishing for Email Prevent Every Fraudulent Message?
Cybercriminals are constantly innovating new ways to commit fraud. Security solutions are only partially foolproof. However, organizations that invest in high-quality technology backed by reputable vendors have a much better security posture than those that don’t.
What is the Best Phishing Protection?
The PhishTitan email filtering solution is a proven cybersecurity tool used by several TitanHQ enterprise customers and managed service providers. It’s well-rated across several sites, and customers praise its ease of use, customer support, and flexibility. PhishTitan is one of the top email filter solutions on the market, and it currently provides protection for large and small businesses.
What is the Best Anti-Phishing Strategy?
Security awareness training is essential for cybersecurity, but relying on users to recognize phishing adds the risk of a data breach from insider threats. Instead of relying on users to recognize phishing, the best anti-phishing strategy is to incorporate an email filtering solution that blocks malicious messages from reaching their intended employee recipients.
What is Anti-Phishing?
Phishing is the largest threat to an enterprise environment, so anti-phishing strategies stop phishing messages from resulting in a data breach. An anti-phishing solution stops email messages from reaching employee inboxes, so corporations significantly reduce their cyber risks by implementing an email filtering solution. Email filtering solutions such as PhishTitan stop malicious messages from being a risk of a data breach.
What Features are in the Best Anti-Phishing Software?
As you search for the best anti-phishing software, find a solution that has features such as artificial intelligence, flexible configurations, notifications to help users, security awareness training incorporated with filtering solutions, good customer support, and operating system agnostic. Anti-phishing software such as PhishTitan is an added layer of security for compliance and data protection.
Do I Need Malware and Phishing Protection?
Any organization that stores sensitive data needs malware and phishing protection. Most organizations have at least some digital assets, so anti-phishing and malware protection are necessary. Malware and phishing are the biggest threats to business data privacy and protection, but the right cybersecurity strategies and email filtering solutions will help reduce the risk of a data breach from these threats.
How can Phishing Solutions Help with Data Protection?
A phishing solution detects any malicious message used for phishing or delivery of malware from an attachment and sends it to a quarantine. Phishing solutions reduce the risks of an enterprise being the victim of a data breach or critical downtime from a ransomware attack. Without phishing solutions, organizations must rely on employees to detect malicious messages, and this increases the risks of a data breach.
Will Email Phishing Solutions Protect my Data?
Every enterprise should use layered cybersecurity strategies. Email phishing solutions are one layer, but this layer is the first defense against malicious email messages. An email phishing filtering solution blocks malicious messages from reaching an employee’s inbox, which removes the threat of phishing altogether. Be prepared for false negatives, but phishing filters block malicious messages from reaching employee inboxes a majority of the time.
What Does Phishing Email Protection Do?
A phishing email protection solution blocks malware, ransomware, malicious scripts, and messages containing embedded links pointing to a phishing website from being sent to employee inboxes. By blocking malicious email messages, organizations reduce the risks of a data breach from email-based threats and add a layer of security to a data protection strategy.
What Does Anti-Spear Phishing Do?
Spear phishing threats target specific high-privileged users within an organization. An anti-spear phishing solution blocks spear phishing messages from reaching employee inboxes. Organizations should use anti-spear phishing software to protect data from email-based attacks and insider threats. Without anti-spear phishing, stolen high-privileged credentials could lead to a massive data breach.
Does Phishing Filters Block Ransomware?
The primary method for ransomware delivery is email. Using targeted spear phishing, attackers send malicious attachments to users or trick them into downloading ransomware on an attacker-controlled domain. Phishing filters quarantine messages meant to deliver ransomware to an organization’s employees. Employees never see the email messages, but administrators can review them in quarantine.
What are the Best Anti-Phishing Solutions?
Several anti-phishing solutions offer features to block messages, but only PhishTitan is a proven highly rated anti-phishing solution that blocks most phishing and malware threats sent using email. PhishTitan closely works with security awareness training solutions to gamify phishing alerts and remove responsibility from employees to help protect them from being the next victim.
What Phishing Filter is Related to SafeTitan?
SafeTitan is a TitanHQ security awareness training solution, and PhishTitan is TitanHQ’s email security software. Both SafeTitan and PhishTitan are related but different products. They work well together to offer organizations an effective way to train employees to identify a phishing threat but automatically block phishing threats using artificial intelligence to reduce inboxing of malicious email messages.
What is Phishing Filter Technology?
Phishing filter technology analyzes incoming organization email messages and uses artificial intelligence to detect potential threats. If a message is considered a threat, the phishing filter technology sends it to a quarantine where administrators can review it. Standard business email is sent to the intended recipient. By blocking malicious messages, organizations greatly reduce the risks of a data breach from malware, ransomware, and phishing sent in emails.
Do I Need Anti-Phishing for Email?
Phishing threats are the start of many of the world’s most damaging ransomware and data breaches. Anti-phishing for email blocks malicious messages from reaching the inboxes of targeted employees that could turn into victims of ransomware, phishing, malware, and other threats. By blocking email messages from reaching user inboxes, the organization protects data from many of today’s current threats and tomorrow’s zero-day threats.

